1992-today: Radon and Progeny studies
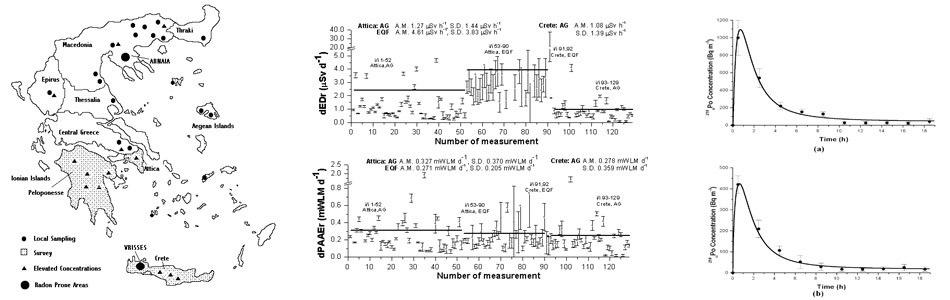
Assistant Professor Dr.Louizi (Department of Medical Physics-National & Kapodistrian University of Athens) and Dr.Nikolopoulos initiated on 1992 research collaboration on the subject of radon focusing on passive indoor measurements in Greece. During that period several calibration experiments were conducted in a specially desgned radon calibration chamber (Mini Radon House), at that time, installed at the Nuclear Technology Section of the National Technological University of Athens. Soon after, the research extended to the measurement of radon progeny concentration in indoor places with active techniques. Product of this research was the collection of a large sample of active and passive measurements in Greece. The active measurements included, later, measurements of radon in water and radon in soil, introducing techniques for the discrimination of radon and thoron. During the last ten years, the radon research focused on thermal spas. After investigating the radon burden of various Greek Spas, the research extended to the dynamical semi-empirical modelling of the Lesvos, Loutraki and Ikaria spas. Measurements and related investigations are still in progress, involving CR-39 and LR-115 detectors. From 2002, additional investigation was implemented in relation to radon precursors prior to earthquakes. Very significant and novel results have been ontained in this subject area, including the recognition of the chaotic-fractal nature of three very signifcant signals of radon in soil detected prior to three signifcant earthquakes occurred in Greece.
1998-2022: Radiation Detectors
The research aims in investigating new sensory material, especially, phosphor and nanophosphor detectors, for potential use in modern medical imaging systems in combination with different optical sensors, The activities include novel computational Monte Carlo methods designed to check the applicability of phosphor and nanophosphor detectors in medical imaging. The outcomes enable (1) the suggestion of optimum phosphor detector-optical sensor combinations under various conditions, and, (2) suggestion of new medical imaging detector designs especially with nanophosphors coupled to CMOS sensors. The whole activity affects (i) industrial medical imaging applications, and (ii) industrial biomedical nanomaterial technology. These benefit also health care services, clinical applications and research, in general. The collaboration include nowadays Prof.Dr. Valais I. and Assis. Prof Dr. Michail (University of West Attica, Department of Biomedical Engineering).
1990-today: Monte Carlo Simulation
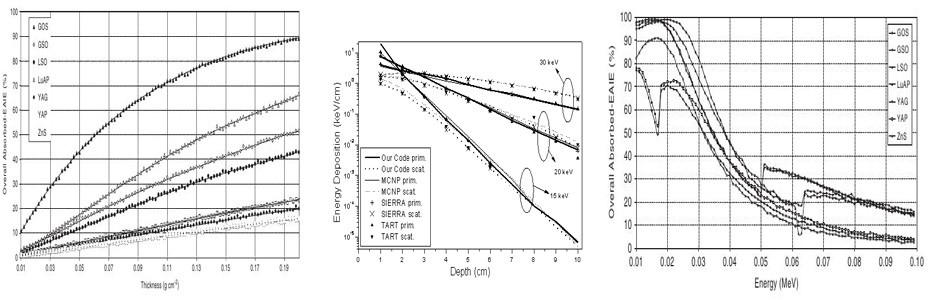
Monte-Carlo modelling initiated on 1992 through a collaboration with the unforgetable Dr. Tzanakos G. and Dr. Angelopoulos A. (f. Profesors,Physics Department, University of Athens). Later, a very close collaboration started with Prof.Dr.Kandarakis I., Prof.Dr. Valais I. and Assis. Prof. Dr. Michail (University of West Attica, Department of Biomedical Engineering) and Prof.Dr.Panayiotakis G. (University of Patras). Today (2020) modelling is implemented through (a) custom designed codes (GNU- gfortran, g++) (b) EGSnrcMP (c) GATE and to some extend (d) MCNP.
2005-today: Electromagnetic Radiation and Radon Emissions from Geo-systems
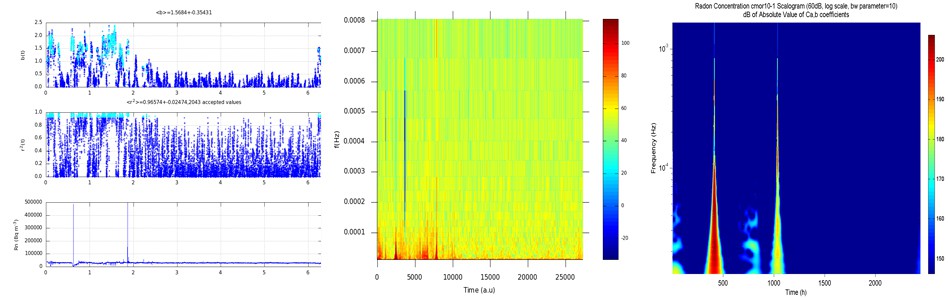
Since 2005 a new collaboration rendered several publiations in the field of telemetric recording and analysis of electromagnetic and radon signals from Geo-systems. Since then, a lot of modelling research has been implemented on the field via: (A) Chaotic Analysis through(i) Spectral fractal wavelet and (ii) Spectral fractal fourier analysis; (B) Long-memory analysis through iii) the Hurst exponent (iv) Rescale Analysis and (v) Detrended fluctuation analysis; (C) Analysis of self-organisation through(vi)Shannon n-block entropy (vii) Shannon n-block entropy per letter (viii) Conditional entropy (ix) Tsallis entropy (x Normalised Tsallis entropy and (D) General signal analysis. Support-vector machines have been employed as well. The overall analysis is performed in the time or frequency domain, through gliding or sliding windowing and vialettering or time-evolution analysis. Today the techniques are applied also to various types of environmental time-series.
2009-today: Electromagnetic Radiation and Digital Communications
Since 2009 new reasearch started on the field of Electromagnetic Radiation Emissions for Digital Communication Systems. The reserach activities include measurements in the following frequence ranges: (a) GSM; (b) DCS; (c) UMTS; (d) DECT; (e) WiFi. Measurements in the TV3, TV4, TV5 and TETRAPOL ranges have also been conducted. Of special concenrn are the Health effects of the mobile communications and the associated emission antenas. A very large dataset has already been collected and is continiously growing. The collaboration include nowadays Dr. Petraki E., Prof. Yannakopoulos P. and others.